 Individually the fields of Digital Identity and Blockchain technologies are both powerful technology trends with a wide spectrum of use case scenarios.
Individually the fields of Digital Identity and Blockchain technologies are both powerful technology trends with a wide spectrum of use case scenarios.
The intersection of the two technologies defines “Identity 3.0”, the foundational infrastructure for the emerging Web 3.0 digital economy and thus a massive growth opportunity.
VentureBeat examines the role that Digital Identity will play in enabling the Web 3.0 economy. They explore example scenarios of Web 3.0 digital business models and the different permutations of Identity architecture that may evolve to facilitate them.
Bain documents a detailed analysis of the landscape: Web3 Could Rewrite the Rules of User Identity, summarizing the trend and how organizations like JPMorgan, Nike, Google, and Disney are pioneering it’s future. As the stack demonstrates the most visible element to end users will be the digital wallets they use to store credentials and other identity services. The Bain article says:
“These wallets act as unified bank accounts and digital passports that have the potential to change how users connect with applications by offering universal sign-in capabilities.”
Decentralized Identity
A commonly agreed architecture principle is that identity will be decentralized; Idenhaus says this will revolutionize Web 3.0. At it’s core is the ‘DID‘ specification from the W3c – Decentralized Identifiers.
“In contrast to typical, federated identifiers, DIDs have been designed so that they may be decoupled from centralized registries, identity providers, and certificate authorities.”
The Decentralized Identity Foundation exists to advance the interests of the decentralized identity community, including performing research and development to advance “pre-competitive” technical foundations towards established interoperable, global standards.
The Amber Group shares this comprehensive overview of decentralized identity and it’s foundation role for Web 3.0, including documenting the four layers it is comprised of, based on the DIF’s 4-Layer Identity Model.
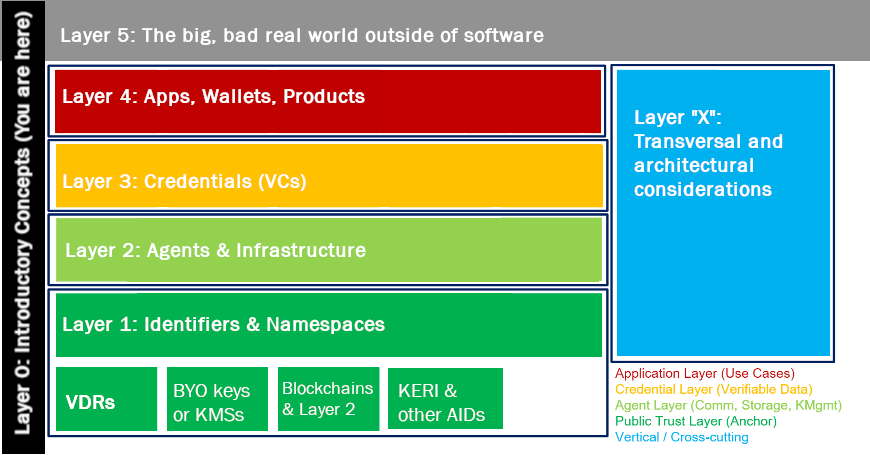
This ecosystem will foster a number of related component part innovations, such as Decentralized PKI and Anonymous Credentials for example. Amber highlights how developments will manifest in the immediate and adapt as it progresses, such as how Goldfinch uses proprietary unique entity checks but aims to leverage decentralized ID solutions when they mature.
Blockchain
It’s also commonly agreed that the Blockchain will play a foundational role in the development of Web 3.0 Identity.
The Global Blockchain Business Council offers this expert panel talk explaining the general role the Blockchain will play in enabling Web 3.0. Speakers from Filecoin, Boson Protocol and Tokens.com describe how Blockchain has the potential to be a driving force as we shift into a web 3.0 world, powering solutions and infrastructures through which we will reimagine the way we envision identity, commerce, and more.
An especially powerful innovation is the role for Blockchain infrastructure to provide an Identity function. For example Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin describes “soulbound tokens” as non-transferable NFTs that can help represent a person’s identity and achievements in Web3.
Another key development is the Ethereum Name Service (ENS), a distributed, open, and extensible naming system based on the Ethereum blockchain. ENS Domains explains:
“ENS has similar goals to DNS, the Internet’s Domain Name Service, but has significantly different architecture due to the capabilities and constraints provided by the Ethereum blockchain. Like DNS, ENS operates on a system of dot-separated hierarchical names called domains, with the owner of a domain having full control over subdomains.
Top-level domains, like ‘.eth’ and ‘.test’, are owned by smart contracts called registrars, which specify rules governing the allocation of their subdomains. Anyone may, by following the rules imposed by these registrar contracts, obtain ownership of a domain for their own use. ENS also supports importing in DNS names already owned by the user for use on ENS.”
We’ll increasingly see innovations emerge that marry these worlds of Identity functions and Blockchain.
For example as Cointribune reported ENS Labs has partnered with Dentity, the leading consumer-first digital identity solution, to bring verifiable credentials onchain to advance real-world access for Web3.
For the first time, ENS users can now securely link their onchain identity with their real-world identity. They can define the scope of the information they wish to share, and maintain complete control over what Personally Identified Information (PII) is publicly accesible, while preventing the need for any PII to be stored onchain.
Conclusion
In conclusion a flagship example of a business pioneering all of these trends is Onyx by JP Morgan. Formed in 2020, Onyx has pioneered the world’s first bank-led blockchain platform for the exchange of value, information and digital assets.
Onyx executives Tyrone Lobban and George Kassis, published this report: Digital Identity – Assessing Web3’s Identity Building Blocks, which provides an excellent summary of all of these concepts and how they have informed JP Morgan’s Web 3.0 market strategy.


















